Burn tokens
Outline
If you wish to burn tokens, then use burn instruction from token program.
In this chapter we will look at most used functionality of token program.
By the end of this chapter, you should know be able burn tokens from token account. The final outcome of this chapter is found here
Prerequisite
For the demonstration purpose, we will retain only create_mint, transfer_mint instructions.
So the remove the following
freeze_token_accountinstructionunfreeze_token_accountinstructiontransfer_token_to_anotherinstructionTransferTokenToAnothercontextUnfreezeTokenAccountcontextFreezeTokenAccountcontext
And remove test cases related to them.
Or you can clone the Chapter-5 repo for getting started immediately.
How to burn tokens ?
We use burn instruction from token_program to destroy minted tokens. Again, only spl_token_mint` authority can perform this action.
Let us follow the 2-step process to burn a token.
- Create a
BurnTokencontext - Write a
burn_tokeninstruction to performburnaction.
Step-1 : Create a BurnToken context ?
Create a BurnToken context using the struct in lib.rs file.
In this code, we burn a token from payer_mint_ata account.
// Burn token
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct BurnToken<'info> {
#[account(
mut,
seeds = [
b"spl-token-mint".as_ref(),
],
bump = vault.spl_token_mint_bump,
)]
pub spl_token_mint: Account<'info, Mint>, // ---> 1
#[account(
seeds = [
b"vault"
],
bump = vault.bump, // --> 2
)]
pub vault : Account<'info, Vault>,
#[account(mut)]
pub payer : Signer<'info>, // ---> 3
#[account(
mut,
associated_token::mint = spl_token_mint,
associated_token::authority = payer
)]
pub payer_mint_ata: Box<Account<'info, TokenAccount>>, // --> 4
pub system_program: Program<'info, System>, // ---> 5
pub token_program: Program<'info, Token>, // ---> 6
pub rent: Sysvar<'info, Rent>, // ---> 7
pub associated_token_program : Program<'info, AssociatedToken>, // ---> 8
}
- We pass the
spl_token_mintaccount without anymutorinitdecoration. - We pass the
vault. Again, this can be used for security purpose. - We pass
payeras thesignerthis time. - We pass
payer_mint_atawhere we want tofreezethe account. system_programaccount for executing the instruction.token_programaccount used for performingfreezeoperationrentmight have to passed as we are usingassociated_token_programassociated_token_programaccount is passed for creating ATA.
With this context, we can invoke a burn instruction.
Step-2 : Create a burn_token instruction ?
We use the burn instruction from token_program to burn tokens. A CPI call is made to token_program to achieve this.
Let us first update the import in lib.rs file
use anchor_spl::{token::{self, Mint, Token, TokenAccount, FreezeAccount, ThawAccount, Burn}, associated_token::AssociatedToken};
Add burn_token instruction.
pub fn burn_token(ctx : Context<BurnToken>) -> Result<()> {
let cpi_context = CpiContext::new(
ctx.accounts.token_program.to_account_info(),
Burn {
from : ctx.accounts.payer_mint_ata.to_account_info(),
mint : ctx.accounts.spl_token_mint.to_account_info(),
authority : ctx.accounts.payer.to_account_info()
},
);
token::burn(cpi_context, 1)?; // we burn 1 token
Ok(())
}
We burn 1 token from payer_mint_ata account.
To test this, let's us write a test case in spl-token.ts file.
Add the following test case in describe block
it("should burn a token of payer wallet ", async () => {
try {
const [splTokenMint, _1] = await findSplTokenMintAddress();
const [vaultMint, _2] = await findVaultAddress();
const [payerMintAta, _3] = await findAssociatedTokenAccount(
payer.publicKey,
splTokenMint
);
const tx = await program.methods
.burnToken()
.accounts({
splTokenMint: splTokenMint,
vault: vaultMint,
associatedTokenProgram: ASSOCIATED_TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
tokenProgram: TOKEN_PROGRAM_ID,
systemProgram: SystemProgram.programId,
payerMintAta: payerMintAta,
rent: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_RENT_PUBKEY,
payer: payer.publicKey,
})
.signers([payer])
.rpc();
console.log("Your transaction signature", tx);
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
}
});
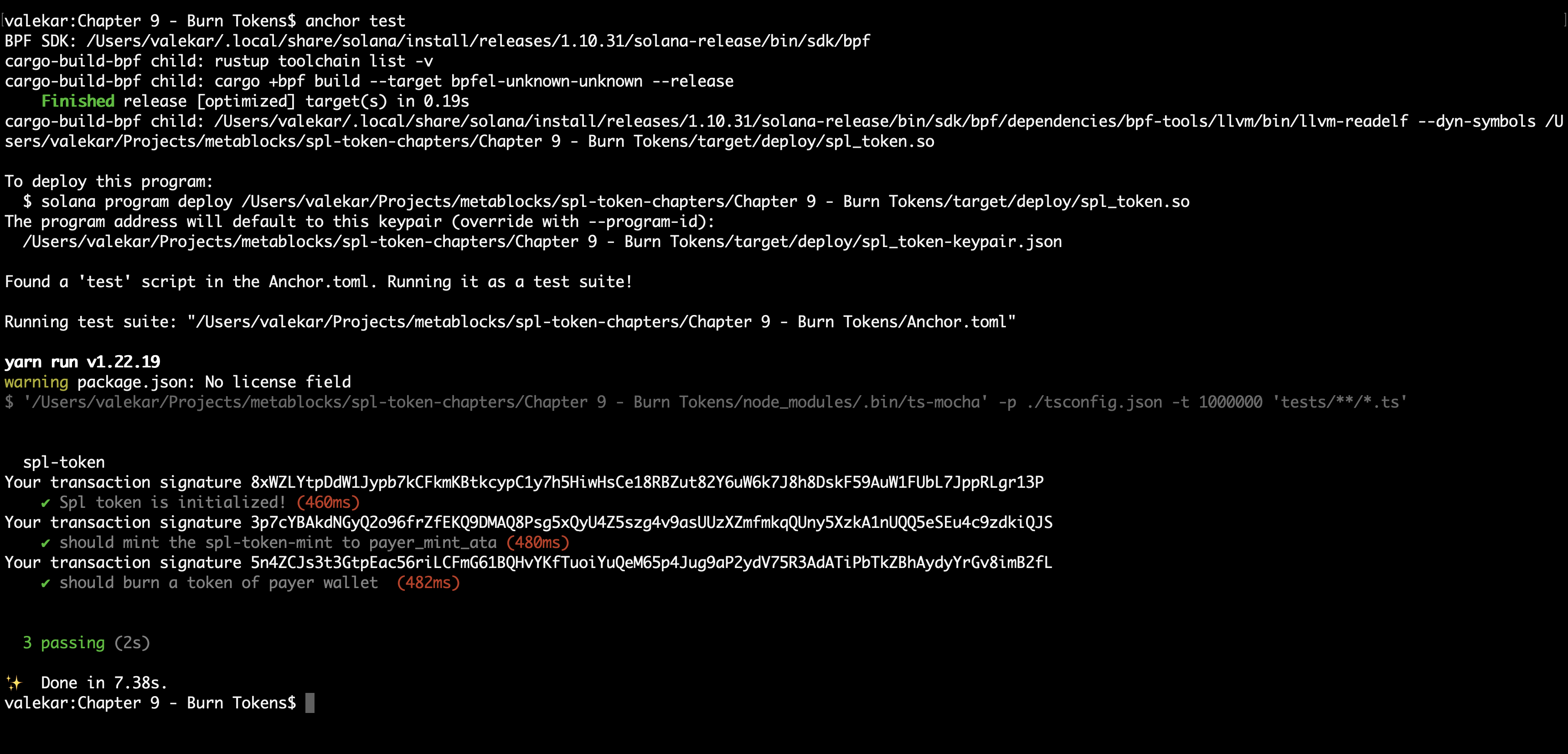
Run the test command
anchor test
With that, we should see the below output with a successfully executed transaction.